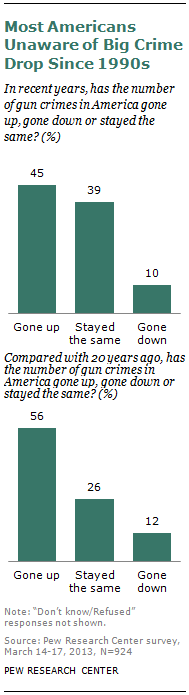While most people are under the impression that gun-related crimes have been skyrocketing in recent years, a new study shows they’ve actually been dropping significantly since their peak in 1993.
The detailed study published by the Pew Research Center shows that contrary to popular belief, America is no longer the Wild West. Since 1993, gun homicides have decreased by 49%, and general violent crime has dipped by an incredible 75%.
The eyes of the nation are glued to firearms politics, but ironically few Americans are aware that gun-related crimes are far less frequent than they were in the past.
According to a Pew survey, 56% of Americans believe gun crime is higher now than it was 20 years ago, while only 12% think it is lower.
It’s difficult to say definitively what has led to this pervasive belief, but it’s likely linked to a lame-stream media pushing gun control every time there’s a high-profile shootings.
It’s also possible that the ever-increasing proliferation of information through social media and online and televised news outlets has made Americans more aware of the world around them, leading them to believe that gun-related crime is on the rise.
Major findings from the Pew Research Center report:
U.S. Firearm Deaths
-
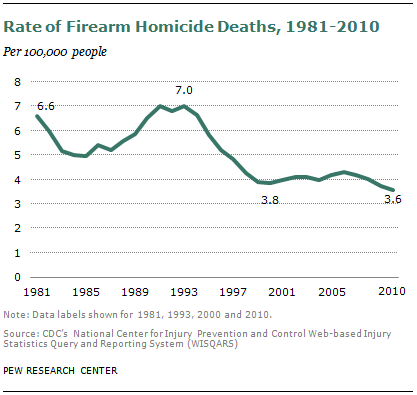
In 2010, there were 3.6 gun homicides per 100,000 people, compared with 7.0 in 1993, according to CDC data.
- In 2010, CDC data counted 11,078 gun homicide deaths, compared with 18,253 in 1993.5
- Men and boys make up the vast majority (84% in 2010) of gun homicide victims. The firearm homicide rate also is more than five times as high for males of all ages (6.2 deaths per 100,000 people) as it is for females (1.1 deaths per 100,000 people).
- By age group, 69% of gun homicide victims in 2010 were ages 18 to 40, an age range that was 31% of the population that year. Gun homicide rates also are highest for adults ages 18 to 24 and 25 to 40.
- A disproportionate share of gun homicide victims are black (55% in 2010, compared with the 13% black share of the population). Whites were 25% of victims but 65% of the population in 2010. Hispanics were 17% of victims and 16% of the population in 2010.
- The firearm suicide rate (6.3 per 100,000 people) is higher than the firearm homicide rate and has come down less sharply. The number of gun suicide deaths (19,392 in 2010) outnumbered gun homicides, as has been true since at least 1981.
U.S. Firearm Crime Victimization
- In 2011, the NCVS estimated there were 181.5 gun crime victimizations for non-fatal violent crime (aggravated assault, robbery and sex crimes) per 100,000 Americans ages 12 and older, compared with 725.3 in 1993.
- In terms of numbers, the NCVS estimated there were about 1.5 million non-fatal gun crime victimizations in 1993 among U.S. residents ages 12 and older, compared with 467,000 in 2011.
U.S. Other Non-fatal Crime
- The victimization rate for all non-fatal violent crime among those ages 12 and older—simple and aggravated assaults, robberies and sex crimes, with or without firearms—dropped 53% from 1993 to 2000, and 49% from 2000 to 2010. It rose 17% from 2010 to 2011.
- Although not the topic of this report, the rate of property crimes—burglary, motor vehicle theft and theft—also declined from 1993 to 2011, by 61%. The rate for these types of crimes was 351.8 per 100,000 people ages 12 and older in 1993, 190.4 in 2000 and 138.7 in 2011.
Context
- The number of firearms available for sale to or possessed by U.S. civilians (about 310 million in 2009, according to the Congressional Research Service) has grown in recent years, and the 2009 per capita rate of one person per gun had roughly doubled since 1968. It is not clear, though, how many U.S. households own guns or whether that share has changed over time.
- Crime stories accounted for 17% of the total time devoted to news on local television broadcasts in 2012, compared with 29% in 2005, according to Pew Research Center’s Project for Excellence in Journalism. Crime trails only traffic and weather as the most common type of story on these newscasts.
(This article was a submission from freelance writer Brent Rogers)